Importance of elevated insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and status of antioxidant vitamins in polycystic ovary disease
Keywords:
Polycystic ovary syndrome , Insulin resistance , Dyslipidemia , Antioxidant vitaminsAbstract
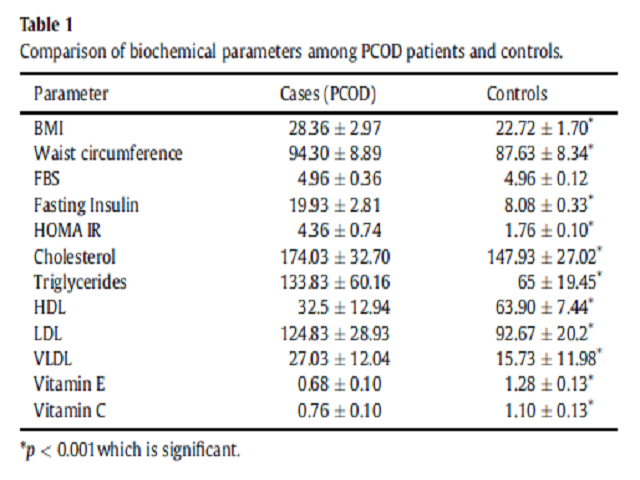
Background: Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common endocrinopathy of child bearing age women with an estimated prevalence of 4e12% and is the leading cause of infertility in females. PCOS is increasingly recognized as a variant of the metabolic syndrome in women with the characteristic features of insulin resistance, central obesity, impaired glucose metabolism, dyslipidemia, and hypertension. Aim: This study is mainly focused on estimation of parameters like insulin resistance, lipid profile and antioxidant vitamins like vitamin C and E in polycystic ovary disease in coastal area of Andhra Pradesh. Materials and methods: The study comprised 45 clinically proven polycystic ovary disease patients in the age range of 18e35 years. The biochemical estimations carried out in the study were e Fasting Blood sugar, Fasting Insulin, HOMA IR, Total cholesterol, Triglycerides, HDL, LDL, VLDL, Vitamin C and E along with anthropometric data. The values obtained were compared with age matched equal number of healthy control female subjects from the same population. Results and discussion: In the present study the levels of total cholesterol, TGL, LDL and, VLDL are increased, whereas mean value of HDL was decreased in PCOS women when compared with healthy controls. The mean values of BMI and waist circumference are also increased. These observations show dyslipidemia and android type of obesity in PCOS subjects. The serum concentration of antioxidant e vitamin E and vitamin C levels are decreased significantly (p < 0.001) when compared to controls. Conclusion: Insulin resistance is predominantly seen in PCOS subjects. The study outlines the importance of insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, decreased antioxidant vitamins in PCOS subjects and oxidative stress may be a cause for the progression of polycystic ovary syndrome.
Downloads
Metrics