Anti-Parkinson Potential of Indian Ocimum species in Relation to Active Components as Revealed Using Metabolites Profiling, in vitro and in silico Enzyme Inhibition Studies
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2023.2.13Keywords:
Parkinson’s Disease, Ocimum species, monoamine oxidase-B, acetylcholinesterase, L-DOPAAbstract
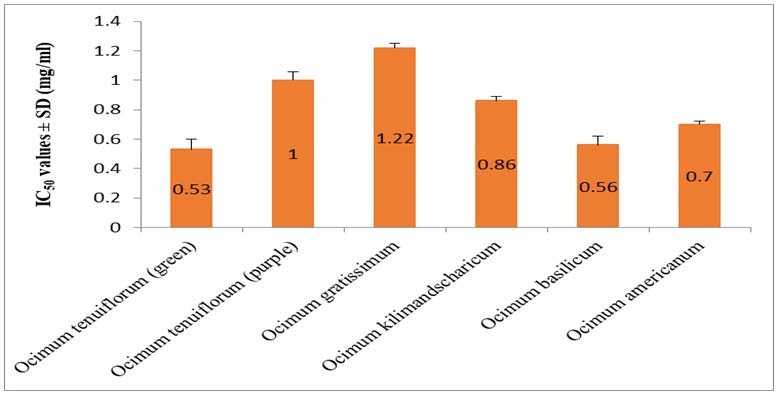
Background: Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is a debilitating neurodegenerative disease suffered by elderly population worldwide. There are different treatment options for its symptomatic relief including the use of inhibitors of monoamine oxidase-B, acetylcholinesterase enzymes and L-DOPA though with certain side effects. Materials and Methods: To identify new resources of natural products with potential effects to treat PD, several Indian Ocimum species, e.g., O. tenuiflorum (green), O. tenuiflorum (purple), O. basilicum, O. americanum, O. kilimandscharicum, and O. gratissimum were screened. Activities of the extracts were studied against monoamine Oxidase-B (MAO-B), and acetylcholinesterase (AChE). Identification of active components present in these extracts was determined using GC-MS and LC-MS metabolites profiling. Further, activity of identified phenolics was measured by docking score against MAO-B and AChE. Results: All extracts and several phenolics showed potential inhibition of these two PD related enzymes based on in vitro and in silico, respectively. Ellagic acid-di-methyl ether-O-glucoside, rosmarinic acid, and luteolin-5-glucuronide were identified as top scoring hits against both AChE and MAO-B from molecular docking studies. L-DOPA was also detected in all the species of Ocimum. Conclusion: IC50 values against both enzymes and L-DOPA levels detected in O. tenuiflorum (green), O. basilicum, and O. americanum pose them as potential nutraceuticals for PD treatment.
Downloads
Metrics