Assessment of the antioxidant and antiradicalic capacities in vitro of different phenolic derivatives
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2014.1.5Keywords:
Antioxidant activity, Radical scavenging, Phenolic derivativesAbstract
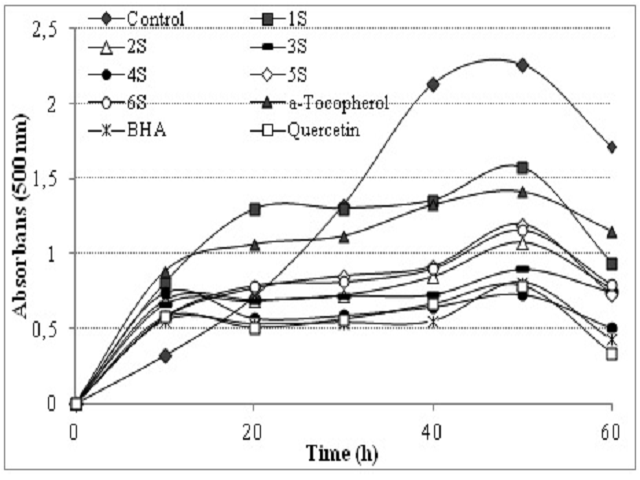
Introduction: The antioxidant and radical scavenging properties of some of the hydroxy phenyl derivatives such as 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid (1), 3-Hydroxy-4-methoxycinnamic acid (2), 3-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2- enoic acid (Sinapic acid) (3), 4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxybenzoic acid (4), 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic acid (Caffeic acid) (5) and 5-Isopropyl-2-methylphenol (6), which are naturally present in fruits and vegetables, were investigated. Methods: The following analysis were conducted: The total antioxidant activity via the ferric thiocyanate method; 2,2’-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzothiazole-6-sulphonate) (ABTS) radical scavenging activity; superoxide anion radical (O2•-) scavenging activity; the total reduction power through potassium ferricyanide reduction method; Cupric ions (Cu2+) reduction capacity through Cuprac method; hydrogen peroxide scavenging activity and chelating activity of ferrous ions (Fe2+). Furthermore, α-tocopherol, butylatedhydroxyanisole (BHA) and quercetin were used as the reference antioxidant compounds. Results: In the comparison of initial states and the products, it’s observed that at the 50th hour the linoleic acid emulsion at 30 μg/mL concentration inhibited the lipid peroxidation by 85%, 60.7%, 69%, 45.4%, 80.4% and 31%, respectively. On the other hand, it’s observed that the linoleic acid emulsion of α-tocopherol, (BHA) and quercetin inhibited the lipid peroxidation by 62.65%, 35.84% and 34.82% respectively, at the same concentration. Conclusions: It’s found as a result of our studies that some of the phenolic compounds such as 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid (1), 3-Hydroxy-4-methoxycinnamic acid (2), 3-(4-Hydroxy-3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-enoic acid (3), 4-Hydroxy-3,5- dimethoxybenzoic acid (4), 3,4-Dihydroxycinnamic acid (5) and 5-Isopropyl-2-methylphenol (6) which are naturally present in foods. They have higher total antioxidant activity, radical scavenging and metal chelating activities than the widely used powerful antioxidant compounds such as BHA, Quercetin and α-tocopherol.
Downloads
Metrics