The Effect of Different Extraction Methods on Antioxidant Capacity and Phytochemical Screening of Syzygium cumini Seeds
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2019.1.9Keywords:
Syzygium cuminix, Syzygium cumini, Extraction, Phytochemical Screening, Antioxidant, DPPH, ABTSAbstract
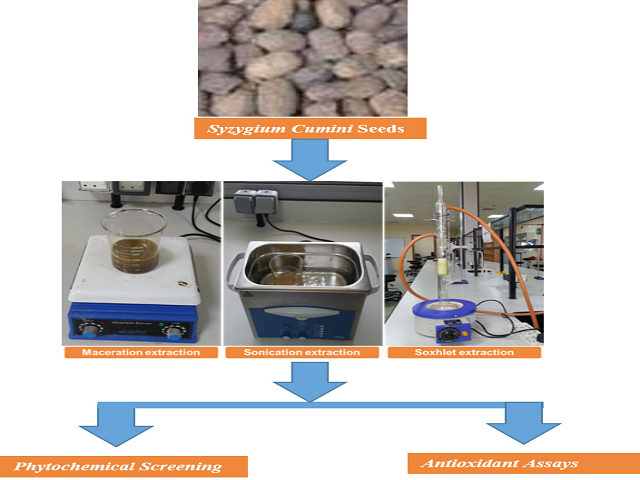
Objective: Syzygium cumini has been used for centuries in traditional medicine for various athological conditions. In the present study, extract yield, phytochemical constituents and in-vitro antioxidant assay ethanolic extracts of Syzygium cumini seeds was investigated. Methods: Extraction techniques like ultrasound microwave assisted solvent, maceration and soxhlet were used for extraction. The extracts were evaluated for potential antioxidant activities by using DPPH and ABTS assay. Results: Our results revealed that extract yield, chemical composition of the extracts and antioxidant activity of the Syzygium cumini extract varied with the extraction process. The results exhibited highest extraction yield and flavonoids, alkaloids and glycoside in ultrasound microwave assisted solvent extraction followed by soxhlet extraction and least in maceration extraction method respectively. All extraction methods showed free radical scavenging potential, ultrasound microwave assisted solvent extraction exhibited significant scavenging potential having an IC50 value of 69 ± 8.11 μg/mL for DPPH and 87 ± 5.86 μg/mL for ABTS. Naringin is used as a reference standard antioxidant agent. Conclusion: These results revealed that the ultrasound microwave assisted solvent extraction of Syzygium cumini seeds can be a rich source of antioxidants containing flavonoids, alkaloids and glycoside. The antioxidants chemical compounds present in Syzygium cumini seeds have various beneficial effects in the phytopharmaceuticals industry.
Downloads
Metrics