Total Phenolic Content, Total Flavonoid Content, In vitro Antioxidant Activity and Antimicrobial Activity against Human Pathogenic Bacteria of Eremurus Himalaicus–An Edible Herb of North Western Himalayas
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.5530/fra.2017.1.14Keywords:
Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, MIC, IC50 value, Total phenolics content, Total Flavonoids contentAbstract
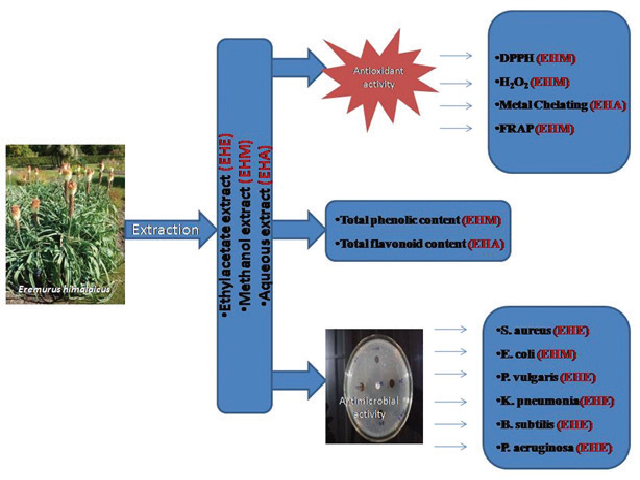
Introduction: A number of plants of Kashmir valley are unexplored and Eremurus himalaicus is one amongst them. Eremurus himalaicus is an edible herb of North Western Himalayas which is yet to be evaluated for possession of antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. Method: The antioxidant potential of the plant extracts (Ethyl acetate, EHE; Methanol, EHM and Aqueous, EHA) was assessed by determining the total phenolic content, total flavonoid content, DPPH (1, 1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl) radical scavenging activity, ferrous metal ion chelating activity, hydrogen peroxide scavenging assay and total reduction capability assay. The plant was further investigated for antimicrobial activity using agar well diffusion method. Results: EHM showed highest total phenolic content followed by EHA and EHE with 270 mg GAE/g, 240 mg GAE/g and 110 mg GAE/g respectively. The flavonoid content was found to be highest in EHA with 85 μg QE/g followed by EHM with 65 μg QE/g and least in ethyl acetate extract with only 20 μg QE/g. Ferrous metal ion chelating potential was also highest for EHA with IC50 value of 200.336. For DPPH assay and H2O2 scavenging assay the activity was highest for EHM with IC50 value of 148.1788 and 182.3371 respectively. In total reduction capability assay again EHM showed highest reducing power. Besides, antibacterial activity was also screened on some human pathogenic bacterial strains where again the highest activity was shown by EHM. Conclusion: In conclusion, EHM and EHA showed highest antioxidant potential and EHE showed the least. Similarly the antimicrobial potential was highest for EHM showing Eremurus himalaicus as a promising new herb for various human diseases.
Downloads
Metrics